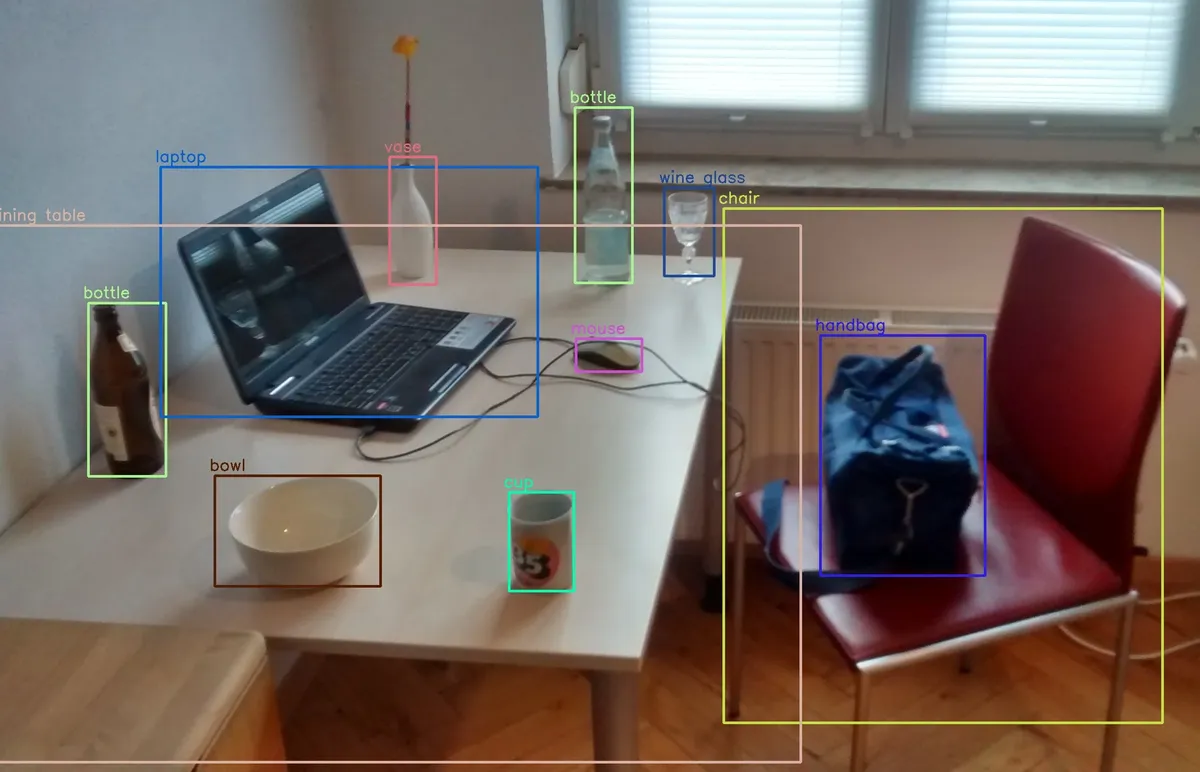
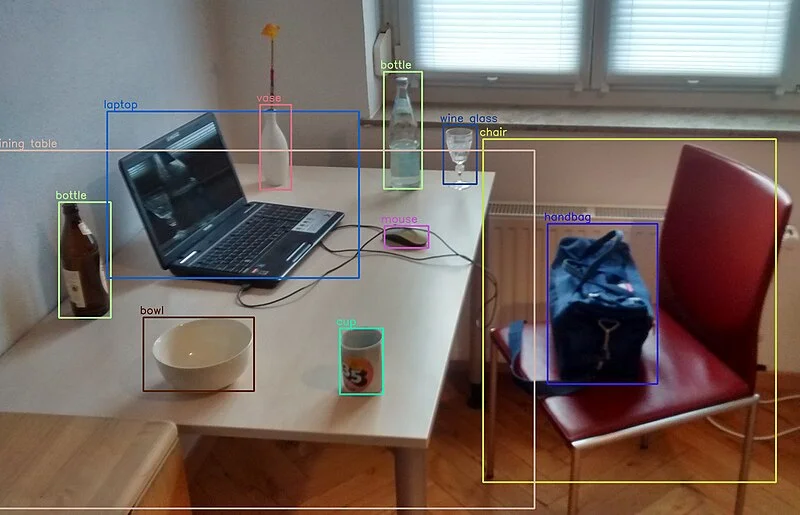
Object Detection on Raspberry Pi
Run real-time object detection on Raspberry Pi using TensorFlow Lite, OpenCV, and optimized models like MobileNet SSD and YOLO.
What You Can Detect
- People counting & tracking
- Vehicle detection
- Animals & pets
- Package detection
- Custom objects (transfer learning)
Required Hardware
| Component | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Raspberry Pi | Pi 4 (4GB+) or Pi 5 |
| Camera | Pi Camera v2 or Arducam |
| Accelerator | Coral USB (optional, 10x faster) |
| Storage | 32GB+ SD card |
Detection Models
| Model | FPS (Pi 4) | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| MobileNet SSD v2 | 10-15 FPS | Good |
| YOLOv5 Nano | 5-8 FPS | Better |
| EfficientDet Lite | 8-12 FPS | Best |
| + Coral TPU | 60+ FPS | Same |
Quick Start Code
import cv2
import tflite_runtime.interpreter as tflite
import numpy as np
# Load model
interpreter = tflite.Interpreter(model_path="detect.tflite")
interpreter.allocate_tensors()
# Camera setup
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
# Preprocess
input_data = cv2.resize(frame, (300, 300))
input_data = np.expand_dims(input_data, axis=0)
# Detect
interpreter.set_tensor(input_details[0]['index'], input_data)
interpreter.invoke()
# Get results
boxes = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[0]['index'])
classes = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[1]['index'])
scores = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[2]['index'])
# Draw boxes for detections > 50% confidence
for i in range(len(scores[0])):
if scores[0][i] > 0.5:
# Draw bounding box
cv2.rectangle(frame, ...)
cv2.imshow('Detection', frame)Applications
Smart Doorbell
Detect people vs packages vs animals
Traffic Counter
Count vehicles, pedestrians, bikes
Wildlife Monitor
Bird/animal identification
Quality Control
Defect detection on production line
Vision Hardware
Browse our Arducam cameras and Raspberry Pi boards.
See also: Raspberry Pi Machine Learning Guide
Frequently Asked Questions
What frame rate can I expect for object detection on Raspberry Pi 4?
With optimized models like YOLOv8-nano or quantized MobileNet-SSD, you can achieve 5-15 FPS on Raspberry Pi 4 at 640x480 resolution. Using a Coral Edge TPU accelerator can boost this to 30+ FPS. Raspberry Pi 5 offers 15-30 FPS without acceleration. Actual performance depends on model complexity, input resolution, and number of objects detected.
Which is better for object detection: TensorFlow Lite or YOLO?
Both have advantages. TensorFlow Lite offers better optimization for ARM processors and compatibility with Coral Edge TPU for massive speedup. YOLO (especially YOLOv8) provides simpler custom training workflows and good real-time performance without acceleration. For maximum speed with TPU, choose TFLite. For easier custom training and good performance without special hardware, choose YOLO.
Can I train custom object detection models on Raspberry Pi?
While technically possible, training is impractically slow on Raspberry Pi. Instead, collect training images with your Arducam camera on the Pi, then transfer them to a powerful machine (preferably with GPU) for training using TensorFlow or PyTorch. After training, export the optimized model and deploy it back to the Raspberry Pi for inference. This workflow gives you custom detection capabilities without the Pi's training limitations.
What camera should I use for fast-moving object detection?
Use an Arducam global shutter camera (like the OV9281 model) for detecting fast-moving objects. Unlike rolling shutter cameras, global shutters capture the entire frame simultaneously, eliminating motion blur and distortion. This is essential for robotics applications, sports analysis, or any scenario where the camera or subjects are in rapid motion.
How can I improve object detection accuracy?
Improve accuracy by: 1) Using higher resolution cameras like Arducam 64MP for distant or small objects, 2) Training custom models on your specific objects and environment, 3) Ensuring proper lighting (add IR illuminators for night vision), 4) Using larger, more accurate models if speed allows (YOLOv8m vs YOLOv8n), 5) Collecting diverse training data covering various angles, lighting, and conditions, and 6) Using proper camera focus and lens selection for your working distance.
